
Pin på Tech History
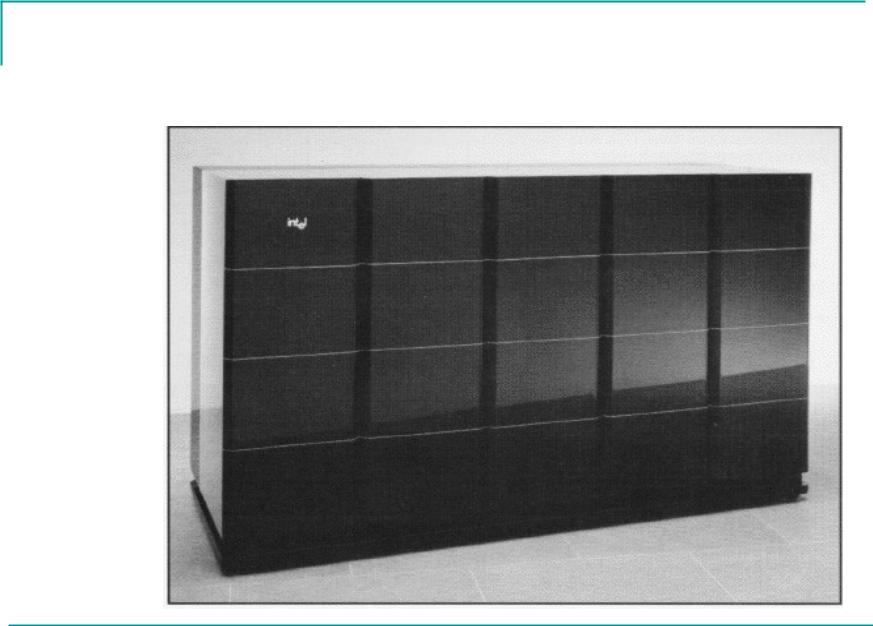
ASCI Red was built by Intel and installed at Sandia National Laboratories in late 1996. The design was based on the Intel Paragon computer. The original goals to deliver a true teraflop machine by the end of 1996 that would be capable of running an ASCI application using all memory and nodes by September 1997 were met. [7]

Новости.
ASCI Red was located at Sandia National Laboratories and built by Intel. Red broke records as the world's first teraFLOPS supercomputer, which means that it could perform 1 trillion floating point operations per second. In addition to its unprecedented speed, the system was acknowledged for its high rate of reliability.

Intel ASCI Red at Sandia National Labs in 1997, the first 1.0 TFLOP
Intel built the first computer in this program, the ASCI Option Red Supercomputer (also known as the Intel TFLOPS supercomputer). This system has over 4500 nodes, 594 Gbytes of RAM, and two independent 1 Tbyte disk systems. Late in the spring of 1997, we set the MP LINPACK world record of 1.34 TFLOPS.

Intel Logos Download
ASCI Red was built by Intel and installed at Sandia National Laboratories in late 1996. The design was based on the Intel Paragon computer. The original goals to deliver a true teraflop machine by the end of 1996 that would be capable of running an ASCI application using all memory and nodes by September 1997 were met.

PPT 第六章 并行处理技术 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4263883
Virgin Cakes: Cassatine di Vergini. Almondy shortbread domes filled with custard and topped with icing, these classic Sicilian sweets were first created in the 1800s at the Monastero di Santa Maria dell Vergini in Palermo.

PPT 高性能计算与网格计算 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4372457
List Rank System Vendor Total Cores Rmax (GFlop/s) Rpeak (GFlop/s) Power (kW) 11/2005: 276: ASCI Red: Intel 9,632

Intel ASCI Red at Sandia National Labs in 1997, the first 1.0 TFLOP
ASCI Red was built by Intel and installed at Sandia National Laboratories in late 1996. The design was based on the Intel Paragon computer. The original goals to deliver a true teraflop machine by the end of 1996 that would be capable of running an ASCI application using all memory and nodes by September 1997 were met. [7]

PPT Cray 1 (1976) PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6783052
June 1993: CM-5/1024 The TOP500 ranking of supercomputers was first published in June, 1993. At that time, the most powerful computer in the world was a CM-5 located in the University of.
Презентация на тему Intel PARAGON/ASCI Red
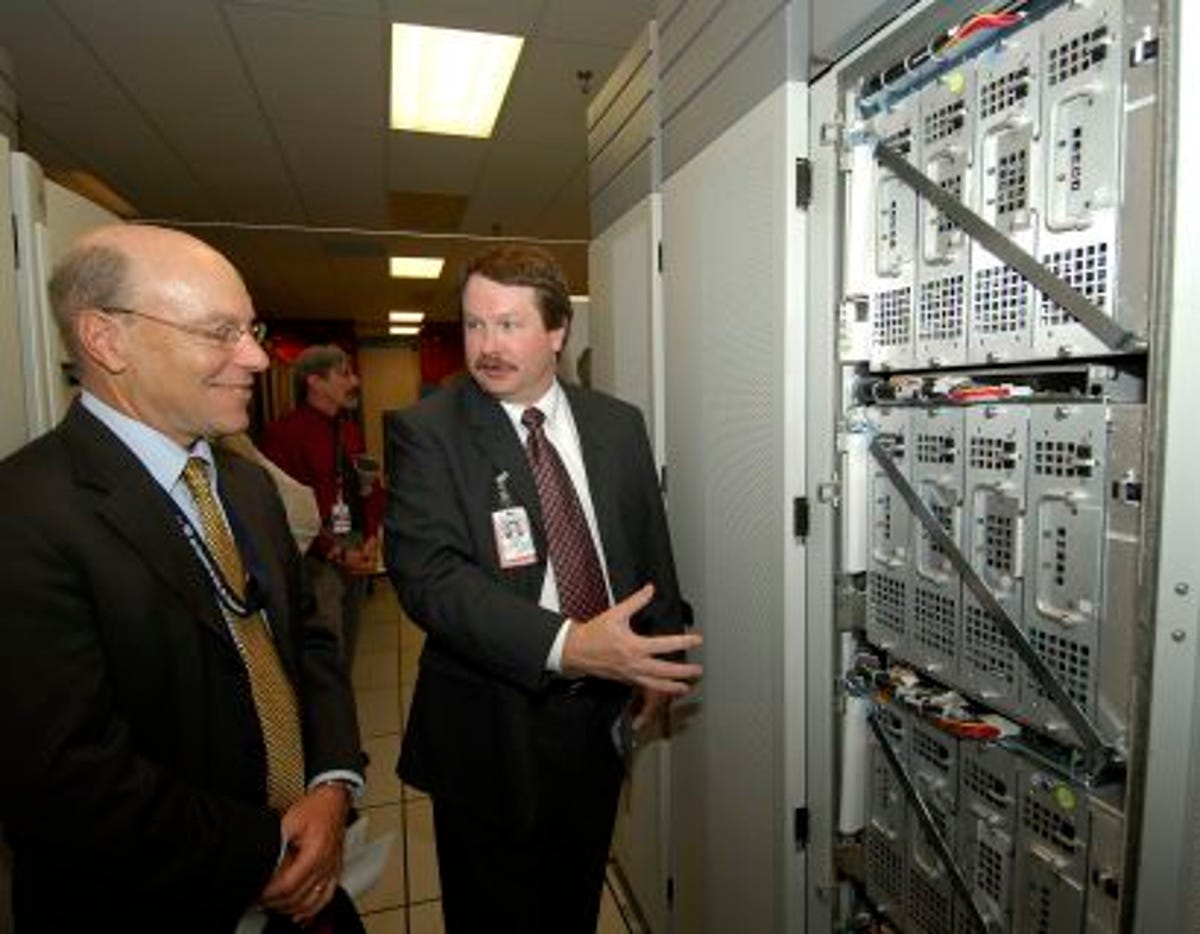
Inside, researchers from Intel and Sandia National Labs were assembling the ASCI Red supercomputer, the first computer capable of doing one trillion calculations per second.

О самых впечатляющих суперкомпьютерах в мире
A Cray-1 supercomputer preserved at the Deutsches Museum The term supercomputing arose in the late 1920s in the United States in response to the IBM tabulators at Columbia University. [citation needed] The CDC 6600, released in 1964, is sometimes considered the first supercomputer.

Intel ASCI Red at Sandia National Labs in 1997, the first 1.0 TFLOP
The ASCI Red TOPS Supercomputer is the first step in the ASCI Platforms Strategy, which is aimed at. MIMD system that Intel is building and installing at Sandia National Laboratories. For more information, contact: SAND96-2659C James L. Tomkins , SNL, 505-845-7249, [email protected] Disclaimer Last modified: October 15, 1999

How Intel's almost used HP chips
Carini, a small town situated in the heart of the island of Sicily, is a place that is often overlooked by tourists. But those who do make the journey to this charming town are rewarded with a unique blend of history, culture, and natural beauty.

Mainframes and From the Beginning Till Today. The CPU Shack Museum
ASCI-Red was a fourth-generation massively parallel supercomputer. It relied on Intel's Pentium Pro processor chips that first came on the market in 1995. This processor allowed the ASCI-Red to achieve the rank of fastest computer in the world on seven seperate occasions, which was unprecedented.

Intel ASCI Red at Sandia National Labs in 1997, the first 1.0 TFLOP
Computers hit the terascale milestone in 1996 with the Department of Energy's (DOE) Intel ASCI Red supercomputer. ASCI Red's peak performance was 1,340,000,000,000 FLOPS, or 1.34 teraFLOPS. Exascale computing is unimaginably faster than that. "Exa" means 18 zeros.

Buy Intel Stock Instead Of AMD (For Now) Intel Corporation (NASDAQINTC) Seeking Alpha
In 1996, computers hit the terascale milestone—that's 12 zeros—when the US Department of Energy's Intel ASCI Red supercomputer was measured at 1.06 teraFLOPS. The Roadrunner supercomputer was the first to pass the petascale milestone (15 zeros) when it was recorded running 1.026 petaFLOPS in 2008.

Cancer app turns to AI to help answer patient questions AI Powered Healthcare Healthcare IT News
Intel ASCI Red 30-second survey No image Report a copyright violation Submit an image you own 1996 Hardware Description ASCI Red (also known as ASCI Option Red or TFLOPS) was the first computer built under the Advanced Strategic Computing Initiative (ASCI). ASCI Red was built by Intel and installed at Sandia in late 1996.